In today’s fast-paced world, where spatial data plays a pivotal role in decision-making, having the right tools for geospatial imaging and analysis is more critical than ever. ERDAS IMAGINE, a flagship software by Hexagon Geospatial, stands out as a game-changer in this domain.
Designed to cater to professionals in remote sensing, photogrammetry, and GIS, ERDAS IMAGINE consolidates cutting-edge functionalities into one intuitive platform, enabling users to extract valuable insights from complex spatial data.
Whether you’re analyzing satellite imagery for environmental changes, processing LiDAR data for urban planning, or creating 3D terrain models for infrastructure development, ERDAS IMAGINE empowers you to achieve unparalleled precision and efficiency.
This blog delves into how ERDAS IMAGINE is revolutionizing the field of geospatial imaging and analysis, making it an indispensable tool for industries ranging from agriculture to disaster management.
ERDAS IMAGINE Software Review
ERDAS IMAGINE is a highly regarded geospatial analysis software suite, primarily used for remote sensing, photogrammetry, and geospatial data processing.
Known for its comprehensive set of tools and robust processing capabilities, it is widely utilized in various industries, including environmental monitoring, urban planning, defense, agriculture, and disaster management.
Here’s an in-depth review of ERDAS IMAGINE, covering its key strengths, weaknesses, and overall usability.
Rating: 4.5/5
1. User-Friendly Interface
While the software is packed with complex tools, it maintains a user-friendly interface that allows both novice and expert users to perform tasks efficiently.
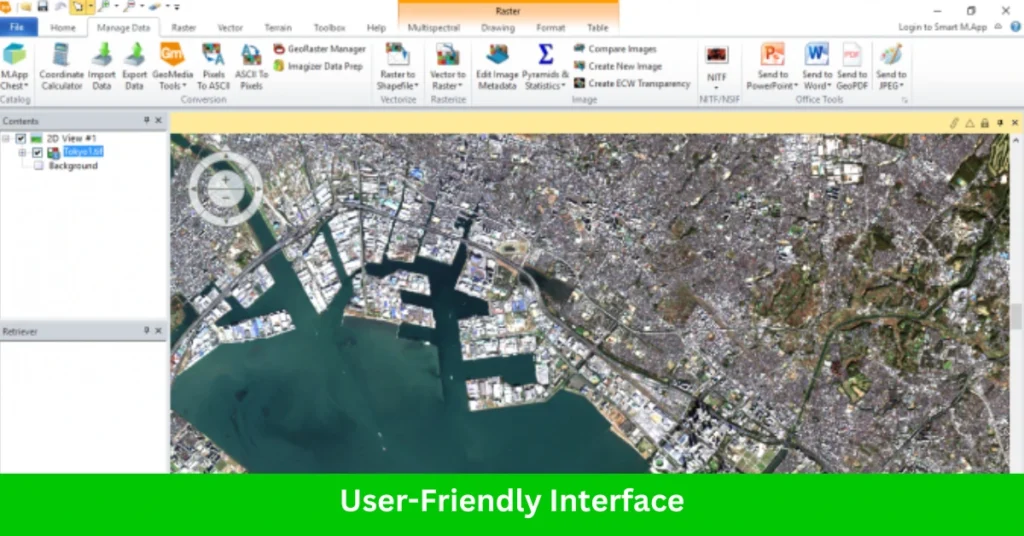
It provides easy access to workflows and supports intuitive tools for managing and analyzing large datasets. The software’s interface can be customized according to user preferences, making it adaptable for different user needs.
2. LiDAR Analysis
With robust tools for LiDAR data, ERDAS IMAGINE facilitates the processing and interpretation of point cloud data for:
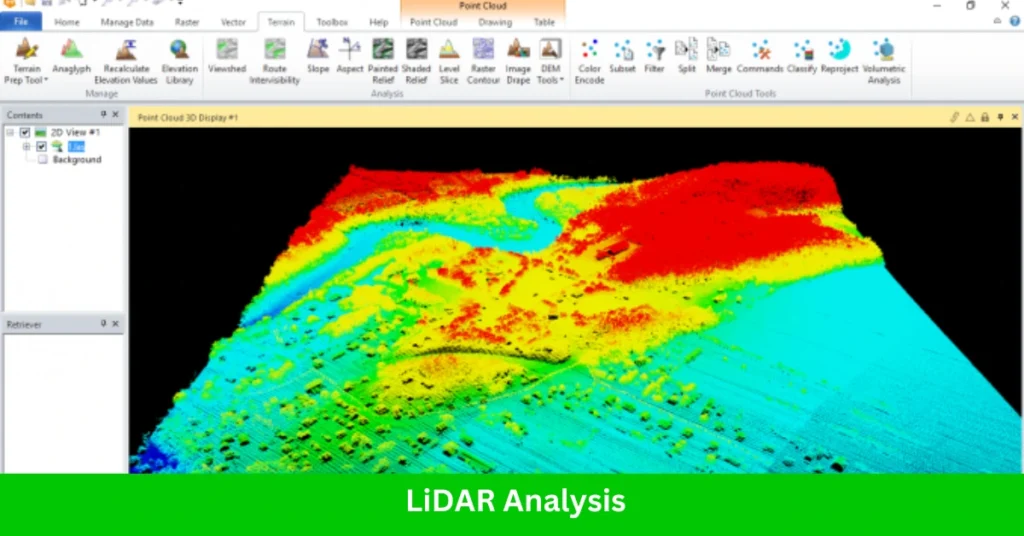
- Terrain and Surface Modeling: Generates detailed terrain and surface models for hydrology, forestry, and urban studies.
- Feature Extraction: Identifies objects like trees, buildings, and power lines from dense point clouds.
- Intensity Analysis: Leverages the intensity values in LiDAR to understand material properties and surface reflectivity.
- Point Cloud Classification: Segments and classifies LiDAR data for applications like vegetation analysis and ground feature delineation.
3. Vector Analysis
While primarily an image processing tool, ERDAS IMAGINE supports vector data integration for hybrid workflows, including:
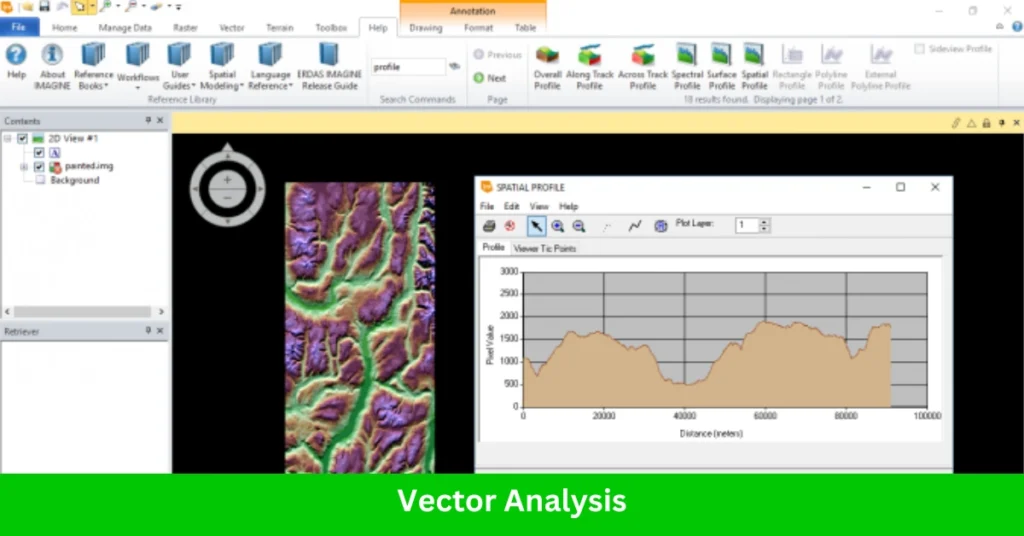
- Overlay Analysis: Combines raster and vector layers for spatial analysis and decision-making.
- Vector Digitization: Allows manual or automated creation of vector features directly on imagery.
- Attribute Management: Facilitates the management and analysis of vector attributes in conjunction with raster datasets.
Read More: Map Maker Interview Questions & Answers
4. Radar Processing
ERDAS IMAGINE provides advanced capabilities for processing radar data, especially Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), making it indispensable for specific applications like:

- Interferometric SAR (InSAR): Creates elevation models or detects surface deformation using radar phase differences.
- Polarimetric Analysis: Analyzes radar polarimetry to classify and interpret surface features.
- Speckle Reduction: Reduces noise in radar imagery while preserving feature integrity.
- Flood Mapping and Disaster Analysis: Uses radar imagery’s ability to penetrate clouds for timely disaster response.
Read More: Field Map Editor Resume Template
5. Remote Sensing
ERDAS IMAGINE is renowned for its ability to process and analyze satellite and aerial imagery with high precision. This functionality includes:
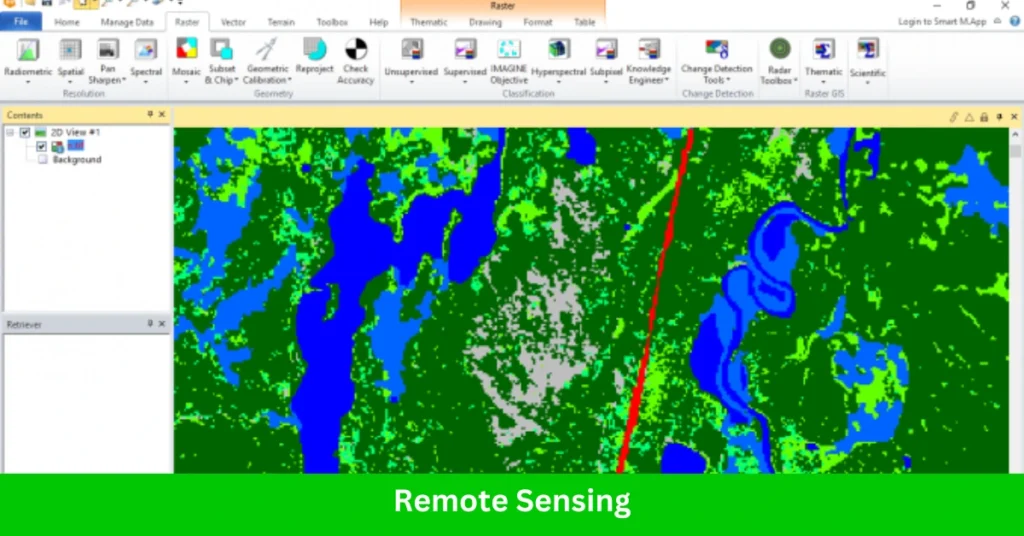
- Image Classification: Supports supervised and unsupervised classification methods to categorize land cover or features.
- Change Detection: Enables users to identify and quantify changes in landscapes over time using multi-temporal imagery.
- Spectral Analysis: Provides tools like spectral indices (e.g., NDVI for vegetation analysis) and advanced spectral libraries for identifying material compositions.
- Orthorectification: Corrects geometric distortions in imagery for accurate spatial representation.
- Hyperspectral and Multispectral Analysis: Allows processing of imagery with hundreds of bands for detailed environmental and material studies.
6. Photogrammetry
ERDAS IMAGINE integrates photogrammetric tools to handle imagery from aerial and drone-based sensors, enabling:
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Generation: Creates elevation models using stereoscopic imagery for terrain analysis.
- Orthophoto Creation: Combines imagery and elevation data to produce spatially accurate, corrected aerial images.
- 3D Feature Extraction: Extracts 3D features like buildings and terrain from imagery, essential for urban planning and infrastructure development.
- Mosaic Production: Merges multiple images into seamless mosaics while maintaining consistent radiometric properties.
Read More: Data Mapper Interview Questions & Answers
ERDAS Imagine History
ERDAS IMAGINE has a rich history rooted in innovation and the advancement of geospatial technology. Over the decades, it has evolved from a pioneering concept to a comprehensive tool, widely recognized for its capabilities in remote sensing, photogrammetry, and GIS. Let’s take a journey through its key milestones:
- 1978 – The Beginning with ERDAS 4
The story began with the release of ERDAS 4 in 1978. Designed to run on Cromemco microcomputers, it was ahead of its time, supporting large digitizing tablets and 80-megabyte hard drives—a significant technological leap for its era. - 1980 – ERDAS 400
Two years later, ERDAS 400 was introduced, marking a step forward in geospatial processing. In an era when computers were both expensive and rare, this system became an essential tool for prestigious organizations such as NASA, the US Forest Service, and the US Environmental Protection Agency. - 1982 – ERDAS 7 and GIS Integration
The release of ERDAS 7 in 1982 was a breakthrough moment for the industry. It facilitated a collaboration with ESRI’s ARC/INFO, linking remote sensing with GIS mapping. This integration allowed users to harness the power of geospatial analysis in entirely new ways. - The Introduction of ERDAS IMAGINE
Building on its legacy, ERDAS IMAGINE was launched as the flagship product, revolutionizing the geospatial industry. The introduction of a graphical user interface (GUI) made it easier than ever for users to visualize spatial data, create maps, and perform sophisticated image processing. - Becoming Part of Hexagon
Today, ERDAS IMAGINE is part of Hexagon’s extensive portfolio, which includes solutions like Hexagon GeoMedia, Leica Geosystems, and M.App Enterprise. This integration has further enhanced its capabilities, cementing its role as a leader in geospatial technology.
Strengths of ERDAS IMAGINE
All-in-One Solution:
ERDAS IMAGINE consolidates functionalities like remote sensing, photogrammetry, LiDAR analysis, and GIS integration in a single product, eliminating the need for multiple software tools.High-Quality Outputs:
The software delivers precise and accurate results, from image classification to 3D modeling, maintaining industry standards.Customizable Workflows:
With robust scripting options and Model Maker (its graphical workflow design tool), users can automate repetitive tasks and design custom workflows.Advanced Visualization Tools:
Includes 2D and 3D visualization features for exploring spatial data in a variety of formats and perspectives.
Use Cases
- Environmental Monitoring: Identifying deforestation, water quality changes, and climate impacts.
- Urban Planning: Analyzing land use, infrastructure development, and population growth.
- Disaster Management: Mapping flood zones, monitoring wildfires, and assessing earthquake impacts.
- Agriculture: Assessing crop health, yield prediction, and precision farming.
Who Should Use ERDAS IMAGINE?
- Environmental Scientists and Geologists: For analyzing satellite and aerial imagery, detecting land-use changes, and studying environmental features like vegetation and soil moisture.
- Urban Planners and Engineers: For creating accurate maps, DEMs, and 3D models of cities or infrastructure.
- Agricultural Researchers: For precision farming, crop monitoring, and land productivity analysis through remote sensing data.
- Government and Defense Agencies: For mapping, land management, and monitoring large-scale projects such as flood detection or disaster response.
Best Alternatives Of ERDAS IMAGINE
- QGIS: Free and open-source, with strong GIS capabilities but limited remote sensing tools.
- ArcGIS Pro: Offers similar functionalities with deeper GIS integration but is equally resource-intensive and costly.
- ENVI: Another popular remote sensing tool, specializing in hyperspectral analysis but less versatile in photogrammetry.
Conclusion
ERDAS IMAGINE is a powerhouse for geospatial professionals, particularly those needing advanced remote sensing and photogrammetric capabilities. While its cost and learning curve might deter casual users, its unmatched breadth of tools makes it indispensable for specialized applications. If you’re looking for an all-in-one solution for imagery analysis, it’s worth the investment.

4 thoughts on “ERDAS Imagine – Revolutionizing Geospatial Imaging and Analysis”