AutoCAD Map 3D seamlessly combines the power of GIS and CAD, offering a unique solution for professionals who need to work with both geospatial and design data. This tool integrates mapping and spatial analysis with traditional CAD features, enabling users to visualize, analyze, and edit spatial data within the familiar AutoCAD environment. Whether you’re in urban planning, infrastructure design, or asset management, AutoCAD Map 3D offers the tools to streamline workflows and enhance collaboration.
In this review, we’ll dive into its key features, pricing, pros and cons, and help you determine if it’s the right solution for your projects.
AutoCAD Map 3D Review
AutoCAD Map 3D is a powerful GIS and CAD software solution that blends the technical capabilities of AutoCAD with advanced mapping and geospatial analysis tools. Aimed at professionals in various industries, including urban planning, civil engineering, and infrastructure development, AutoCAD Map 3D provides a unified platform for creating, managing, and analyzing geospatial data.
Rating: 4.6/5
Pros and Cons of AutoCAD Map 3D
Pros
All-in-One Solution: The combination of GIS and CAD tools in one software makes AutoCAD Map 3D a versatile choice for professionals who need to work with both types of data.
Intuitive Interface: The software retains AutoCAD’s familiar user interface, which helps users transition to AutoCAD Map 3D with ease, reducing the learning curve.
Customization: AutoCAD Map 3D is highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs through custom tools and scripts.
Strong Data Management Capabilities: AutoCAD Map 3D excels in managing large datasets, ensuring users can handle complex projects without performance issues.
Cons
Cost: AutoCAD Map 3D can be expensive, especially for small businesses or individuals. The pricing may be a barrier for those on tight budgets.
Complexity for Beginners: While the software is powerful, its many features and capabilities can be overwhelming for new users, especially those without a strong GIS or CAD background.
Limited 3D Visualization Tools: Compared to other 3D modeling software, AutoCAD Map 3D’s 3D visualization capabilities are somewhat limited, which may be a drawback for users who require more advanced 3D features.
Key Features of AutoCAD Map 3D
- Seamless GIS and CAD Integration: AutoCAD Map 3D allows users to work with both CAD designs and GIS data in one environment. This integration helps users visualize spatial data and incorporate geographic context into their CAD projects.
- Geospatial Data Management: Users can connect to various geospatial data sources, such as shapefiles, rasters, and databases, to manage and analyze large volumes of spatial data efficiently.
- Advanced Mapping Tools: AutoCAD Map 3D includes a wide range of tools for map creation, spatial analysis, and data management, allowing users to generate detailed, customized maps with ease.
- Data Connectivity: The software allows users to connect to external databases and geospatial sources, ensuring that all project data remains up-to-date and integrated across platforms.
- Infrastructure and Asset Management: With built-in tools for asset management, users can track, manage, and maintain infrastructure projects more effectively by tying spatial data to CAD models.
CAD and GIS Fusion
AutoCAD Map 3D effectively combines the functionalities of both CAD and GIS, offering powerful tools for mapping, spatial analysis, and data management. The software provides a ribbon-based interface with dedicated tabs for tasks like map layout design, GIS analysis, and feature editing, making it easier for users to navigate between different functions.
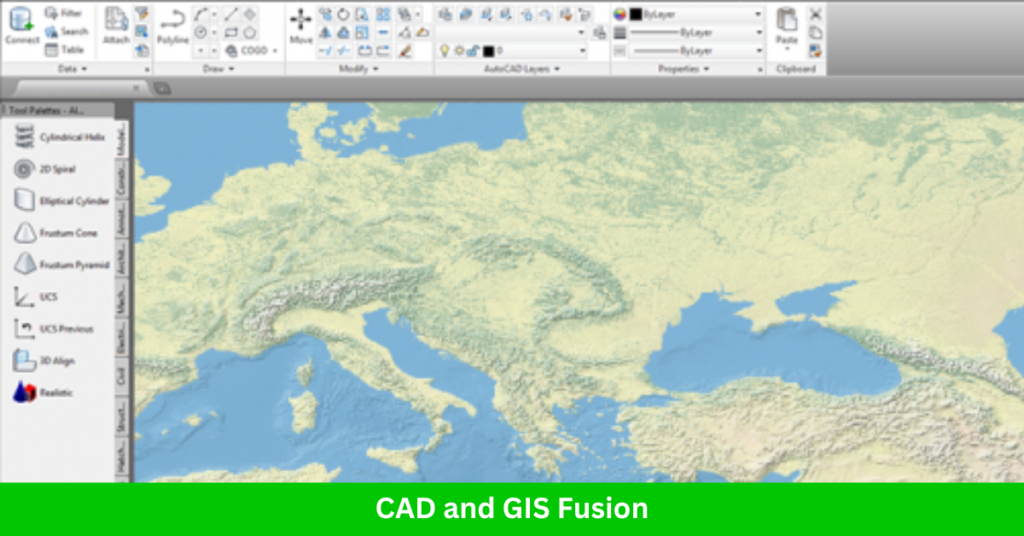
While AutoCAD Map 3D provides capabilities for both CAD and GIS workflows, it doesn’t specialize in either field exclusively. Instead, it serves as a bridge, offering essential features from both disciplines. For users looking to enhance its GIS capabilities, the ArcGIS for AutoCAD plugin can be used to improve interoperability, allowing seamless integration of GIS data and image services for enhanced editing and spatial analysis.
History of AutoCAD Map 3D
AutoCAD Map 3D, developed by Autodesk, has evolved significantly since its inception to become one of the leading tools for integrating GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) in a single platform. Here is a brief history of how AutoCAD Map 3D came to be:
Early Beginnings – 2000s: AutoCAD Map 3D was first introduced in the early 2000s, initially as a standalone GIS product designed to complement Autodesk’s core AutoCAD software. Its purpose was to provide users with tools to integrate geospatial data into their AutoCAD drawings. The initial versions focused on enhancing map production, spatial analysis, and providing access to geographic data from a variety of sources, such as shapefiles and databases.
2004 – First Major Version: In 2004, AutoCAD Map 3D saw its first significant upgrade. This version allowed for the creation of more sophisticated maps, leveraging AutoCAD’s existing drafting tools while adding GIS-specific functionalities. Users could now directly manipulate and manage geospatial data, allowing for smoother integration of maps into the design process. The integration of Map 3D into AutoCAD’s existing ecosystem made it a practical choice for industries where both CAD and GIS tools were essential.
2007 – Integration with Autodesk Infrastructure Solutions: AutoCAD Map 3D began to integrate more tightly with other Autodesk solutions, such as AutoCAD Civil 3D, for infrastructure design and management. This enabled better coordination between mapping, design, and project management teams. The software also expanded its capabilities to include geospatial database connectivity, which allowed users to interact with spatial data stored in databases such as Oracle Spatial or Microsoft SQL Server.
2010 – Expanded GIS Capabilities: By 2010, AutoCAD Map 3D had grown to include advanced GIS capabilities, such as the ability to perform spatial analysis, manage large datasets, and perform geospatial data processing tasks. These updates were crucial for users in the utilities, transportation, and urban planning sectors, where the need for combining GIS data with engineering designs was more critical than ever.
2013 – Continued Enhancements: In subsequent releases, Autodesk continued to add functionality and improve performance, with a focus on better integration with other Autodesk products and greater support for cloud-based workflows. This allowed users to access their data from anywhere, facilitating collaboration across multiple disciplines and industries.
Present Day (2020s): AutoCAD Map 3D continues to be a key player in the GIS and CAD integration space. Its recent versions focus on improving the user experience with a more intuitive interface and powerful data management capabilities. The software now supports advanced data formats and offers greater compatibility with modern GIS data sources, making it an essential tool for industries such as urban planning, infrastructure design, and environmental management.
Strengths of AutoCAD Map 3D
AutoCAD Map 3D is a robust tool that offers a unique combination of CAD and GIS functionality. Its integration of geographic information systems into AutoCAD provides a powerful solution for professionals in various fields such as urban planning, engineering, and infrastructure management. Here are some of the key strengths of AutoCAD Map 3D:
Seamless Integration of CAD and GIS: AutoCAD Map 3D excels at combining GIS capabilities with the drafting and design tools of AutoCAD. This integration enables professionals to work with both geographic and engineering data in a single platform, improving workflow efficiency and coordination across teams.
Broad Data Compatibility: One of the key advantages of AutoCAD Map 3D is its ability to work with a wide range of data formats, including shapefiles, raster data, geospatial databases, and more. It supports numerous industry-standard file formats, ensuring that users can easily import and export data from different sources without compatibility issues.
Powerful Spatial Analysis Tools: AutoCAD Map 3D offers a range of spatial analysis tools that help users perform tasks like proximity analysis, buffering, and overlay analysis. These tools are particularly useful for urban planning, environmental analysis, and infrastructure management, enabling better decision-making based on geographic data.
Customizable and Extensible: The software provides a high degree of customization, allowing users to tailor their workflow to suit their specific needs. It supports the creation of custom map layouts, symbology, and labeling, giving professionals the flexibility to represent spatial data exactly how they need it. Additionally, AutoCAD Map 3D can be extended through scripting and third-party add-ons, offering more functionality for specialized tasks.
Data Management Capabilities: AutoCAD Map 3D has robust data management features, including support for geodatabases and integration with Autodesk’s cloud-based solutions. This ensures that large datasets can be efficiently stored, queried, and accessed across different projects and teams. Users can easily update and manage data, enhancing collaboration and streamlining workflows.
Use Cases of AutoCAD Map 3D
AutoCAD Map 3D is a versatile tool used across various industries for tasks that require both spatial data management and detailed design work. Here are some common use cases where AutoCAD Map 3D excels:
Urban Planning and Development: Urban planners use AutoCAD Map 3D to design, visualize, and manage infrastructure projects. The software’s ability to handle GIS data, such as zoning maps, land use, and transportation networks, combined with CAD capabilities, helps create accurate plans for cities and urban developments. Planners can analyze spatial data to determine the best locations for new projects and ensure compliance with zoning regulations.
Transportation and Infrastructure Design: Engineers in transportation and infrastructure projects rely on AutoCAD Map 3D to create detailed roadways, railways, and utility networks. The software enables them to model 3D road layouts, simulate traffic flows, and assess the impact of new developments on existing infrastructure. It’s also used for asset management, helping track and maintain roads, bridges, and utility systems over time.
Utility and Pipeline Management: AutoCAD Map 3D is widely used in the utilities sector for mapping and managing water, gas, electricity, and sewer systems. The software allows for the creation of accurate, scalable maps of utility networks, including pipelines and power lines, helping teams with asset management, maintenance planning, and network optimization. It can also be used to identify the most efficient routing for new pipelines or utilities.
Environmental and Natural Resource Management: Environmental scientists and resource managers use AutoCAD Map 3D to map and analyze natural resources such as forests, wetlands, and watersheds. The software’s spatial analysis tools allow users to assess environmental factors, plan conservation efforts, and model the impact of development projects on the environment. GIS data on terrain, vegetation, and wildlife habitats can be incorporated into detailed maps to assist with land-use planning and policy decisions.
Land Surveying and Cartography: Land surveyors and cartographers benefit from AutoCAD Map 3D’s ability to integrate survey data with CAD tools for creating accurate maps. Survey data such as topographic features, property boundaries, and easements can be mapped and analyzed to support real estate transactions, land development, and government planning. Cartographers can also use the software to produce detailed, high-quality maps for various purposes, including print publications and digital platforms.
Who Should Use AutoCAD Map 3D?
AutoCAD Map 3D is ideal for:
Urban Planners and Developers: AutoCAD Map 3D is perfect for professionals in urban planning and development who need to design and manage infrastructure, utilities, and land use in both 2D and 3D formats.
Civil Engineers and Surveyors: Engineers and surveyors use AutoCAD Map 3D for its precise mapping, detailed terrain analysis, and ability to integrate survey data with CAD drawings for infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and utility networks.
Utility and Telecom Professionals: With its advanced tools for mapping and managing utility and telecom infrastructure, AutoCAD Map 3D is highly suited for professionals in the utilities sector, helping them track assets, plan network expansions, and ensure proper maintenance.
Environmental Scientists: Professionals in environmental sciences, forestry, and land management benefit from AutoCAD Map 3D’s ability to handle complex geospatial data and visualize environmental changes, such as water flow, vegetation cover, and topography.
Real Estate Developers: Real estate professionals use AutoCAD Map 3D for site planning, mapping property boundaries, and assessing infrastructure needs to ensure optimal development decisions.
When to Use AutoCAD Map 3D?
AutoCAD Map 3D is a versatile GIS and CAD tool, ideal for users who:
Need a Fusion of GIS and CAD: Perfect for those who need to integrate spatial data with CAD designs, making it ideal for urban planning, engineering, and construction projects.
Work with Infrastructure Projects: Suitable for professionals focused on designing, managing, and analyzing infrastructure networks like roads, utilities, and telecoms with accurate geospatial data and CAD features.
Require Precision in Design and Mapping: Best for users who need high-precision in terrain modeling, mapping boundaries, or working with survey data for civil engineering projects.
Focus on Asset Management: Ideal for managing and visualizing assets like utility lines, pipelines, and building structures, making it essential for industries like utilities, construction, and telecommunications.
Prefer an Industry-Standard CAD Solution with GIS Capabilities: A great choice for professionals who are already familiar with AutoCAD but need to integrate GIS functions for spatial analysis and management of geospatial data.
Best Alternatives to AutoCAD Map 3D
Here are three of the best alternatives to AutoCAD Map 3D:
1. ArcGIS Pro
Best For: Comprehensive GIS tasks with strong spatial analysis, 3D modeling, and high-quality mapping.
Best For: Open-source GIS with a strong community and wide array of plugins.
3. Bentley Map
Best For: Infrastructure and engineering projects requiring integration of GIS and CAD data.
Conclusion: AutoCAD Map 3D
AutoCAD Map 3D stands out as a robust solution for users who require the seamless integration of CAD and GIS functionalities. Its ability to work with spatial data and create detailed maps while leveraging the power of AutoCAD makes it an excellent choice for professionals in industries like urban planning, engineering, and construction. The software excels in combining the precision of CAD with the analytical capabilities of GIS, allowing users to visualize and analyze complex data sets with ease.
Despite the rise of more specialized GIS tools, AutoCAD Map 3D remains a valuable asset for teams that need both CAD drafting and GIS mapping in one platform. Its extensive toolset, coupled with its compatibility with other Autodesk products, ensures that it can support diverse workflows, from designing infrastructure to performing advanced geospatial analysis.
2 thoughts on “AutoCAD Map 3D – GIS and CAD Fusion”